08045475244
Most Popular Products
|
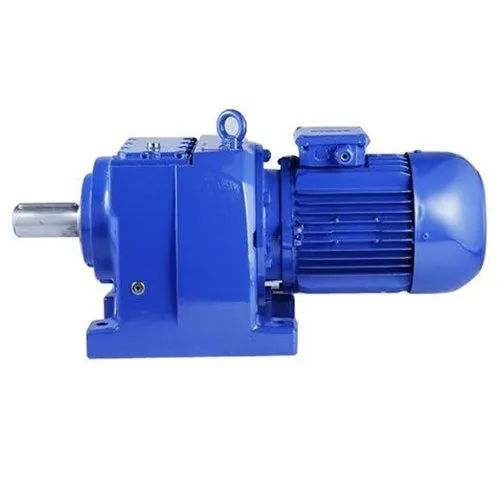
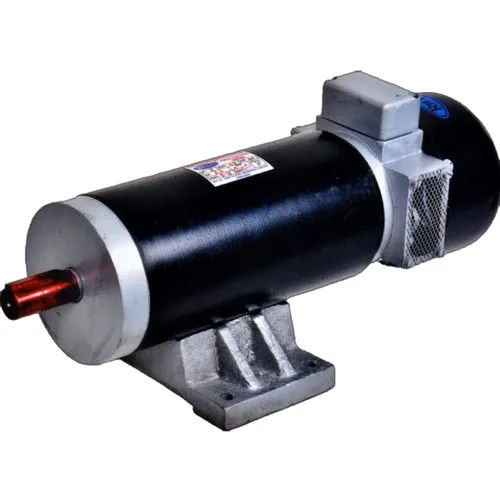
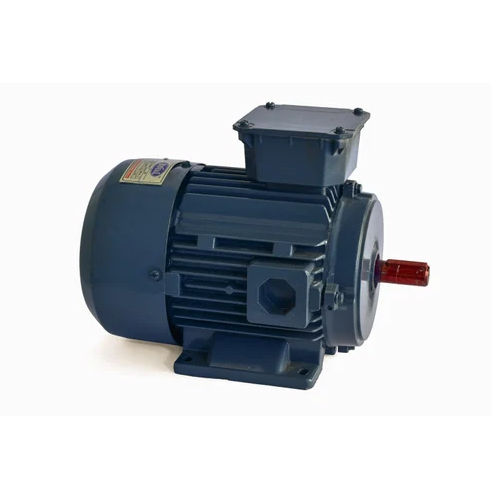
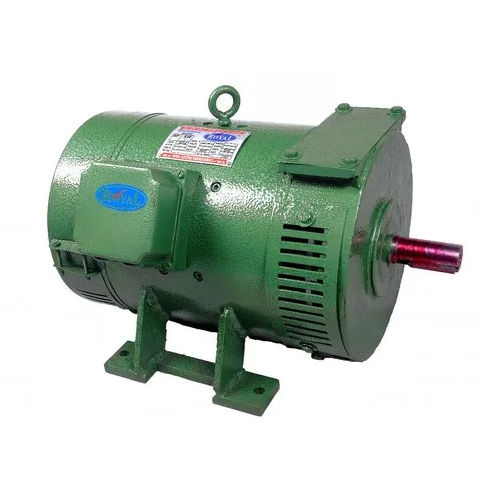
Electric MotorAn electromechanical device that transforms electrical energy into mechanical energy is an electric motor. It is made up of a revolving component called the rotor and a stationary component called the stator. The rotor of the motor rotates when an electric current passes through its coils, producing a magnetic field that interacts with the rotor's magnets to produce rotation. Due to their effectiveness, dependability, and capacity to provide exact control over rotational motion, electric motors are extensively employed in a wide range of applications, from home appliances to industrial gear and transportation systems.
|
|
|
|
|
×
Add a mobile number to receive call from "ROYAL ELECTRIC ENGINEERING CO."
×
Enter OTP
×
Share additional details for a quick response
×
Thank You!
Thank You for your valuable time. We have received your details and will get back to you shortly.
×
Get a price quote for 2 Hp DC Electric Motor
×
Contact Details
ROYAL ELECTRIC ENGINEERING CO.
GST : 24AALPP3082A1ZZ
GST : 24AALPP3082A1ZZ
38, Giriver Globe Industrial Park, Vishala Road, Nr. Shree Ram Estate, S. P. Ring Road, Ahmedabad - 382415, Gujarat, India
Phone :08045475244
 |
ROYAL ELECTRIC ENGINEERING CO.
All Rights Reserved.(Terms of Use) Developed and Managed by Infocom Network Private Limited. |
✕
Contact Us
Name
Comapny Name
Phone Number
Email Id
City / State

OTP Verification
Verification Code
Did not receive yet?
Resend OTP

Thank you!
We have received your requirements
For an immediate response, please call this
number 08045475244
✕
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email
Name
Comapny Name
Phone Number
Email Id
City / State
Confirm Your Requirement
Verification Code
Did not receive yet?
Resend OTP

Youre Done!
We have received your requirements and will reply shortly with the best price.
Products You May Like